Solution Viscosity is the measurement of the resistance to flow of a polymer solution. Solution viscosity can be expressed as relative, specific, absolute, kinematic, inherent and intrinsic viscosities. Solution viscosity is typically measured in a capillary viscometer such as an Ostwald or Ubbelohde viscometer. The fundamental property measured is the time required by the solution to flow between two level marks on the capillary. The time is then related to the viscosity. For the relative viscosity, the equation is:
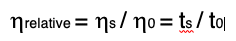
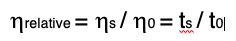
Where ts is the flow time for the sample solution and t0 the flow time for the solvent.
The follow table summarizes the various viscosity averages:
| VISCOSITY AVERAGE |
UNITS |
EQUATION |
| Relative Viscosity |
dimensionless |
_ r = _ / _ 0 |
| Specific Viscosity |
dimensionless |
_ sp = _ r - 1 |
| Inherent Viscosity |
dL/g |
_inh = (ln _ r)/C |
| Reduced Viscosity |
dL/g |
_red = _ sp/C |
| Intrinsic Viscosity |
dL/g |
[_] = (_ sp/C)_C_0 |
| Absolute Viscosity |
centipoise |
_ = _r X _solvent |
| Kinematic Viscosity |
centistokes |
_k = _/density |
| _ = Solution Viscosity, _0 = solvent viscosity |
|