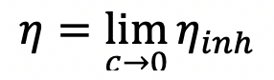Intrinsic Viscosity is the hypothetical inherent viscosity of a solute at infinite dilution. It can be written as:
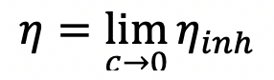
Where η represents the intrinsic viscosity of the solute, c represents the concentration of the solute and ηinh represents the inherent viscosity of the solution. Intrinsic viscosity can be used to determine the molecular weight of a polymer using the Mark-Houwink equation. To determine intrinsic viscosity, several solutions of the solute are prepared at different concentrations. The inherent viscosity of each solution is then measured and plotted as a function of concentration. The y-intercept of this plot is the intrinsic viscosity. The units of intrinsic viscosity are typically deciliters per gram (dL/g), or inverse concentration and can also be viewed as an indication of molecular density for a polymer under a given set of conditions (solvent composition and temperature).
- Quality control tool for polymers
- Determine viscosity average molecular weight of polymers
- Examines polymer architecture (branching)